Advanced manufacturing
for advanced applications

October 8th. 2024
Advanced Manufacturing
for advanced applications
Additive manufacturing refers to processes in which the geometry is no longer generated by physical tools, but is instead created on the basis of numerical control data. This innovative method offers a high degree of flexibility and geometric freedom. Furthermore, the material is created or significantly modified during the process. In contrast to conventional machining processes, quality assurance for the mechanical and technological properties of the finished products cannot be transferred exclusively to the feed stock material manufacturer. In fact, depending on the perspective, the component manufacturer may even become a material manufacturer. In these special processes (see e.g., ISO 9001), quality assurance and proof of machine capability are of paramount importance.
Additive manufacturing, once used for the production of illustrative material, prototypes and functional samples, has rapidly developed within a short time into a process that is used for the production of high-performance components in safety-critical applications.
Examples include aircraft turbines, rocket engines and hydraulic valves. The use of high-performance materials such as Inconel, titanium, high strength aluminum alloys and tool steels is crucial, as is the expansion of additive manufacturing to large-volume applications with high price pressure regarding the material, such as pressure vessels, steel components or components in crane construction.
Additive manufacturing refers to processes in which the geometry is no longer generated by physical tools, but is instead created on the basis of numerical control data. This innovative method offers a high degree of flexibility and geometric freedom. Furthermore, the material is created or significantly modified during the process. In contrast to conventional machining processes, quality assurance for the mechanical and technological properties of the finished products cannot be transferred exclusively to the feed stock material manufacturer. In fact, depending on the perspective, the component manufacturer may even become a material manufacturer. In these special processes (see e.g., ISO 9001), quality assurance and proof of machine capability are of paramount importance.
Additive manufacturing, once used for the production of illustrative material, prototypes and functional samples, has rapidly developed within a short time into a process that is used for the production of high-performance components in safety-critical applications.
Examples include aircraft turbines, rocket engines and hydraulic valves. The use of high-performance materials such as Inconel, titanium, high strength aluminum alloys and tool steels is crucial, as is the expansion of additive manufacturing to large-volume applications with high price pressure regarding the material, such as pressure vessels, steel components or components in crane construction.

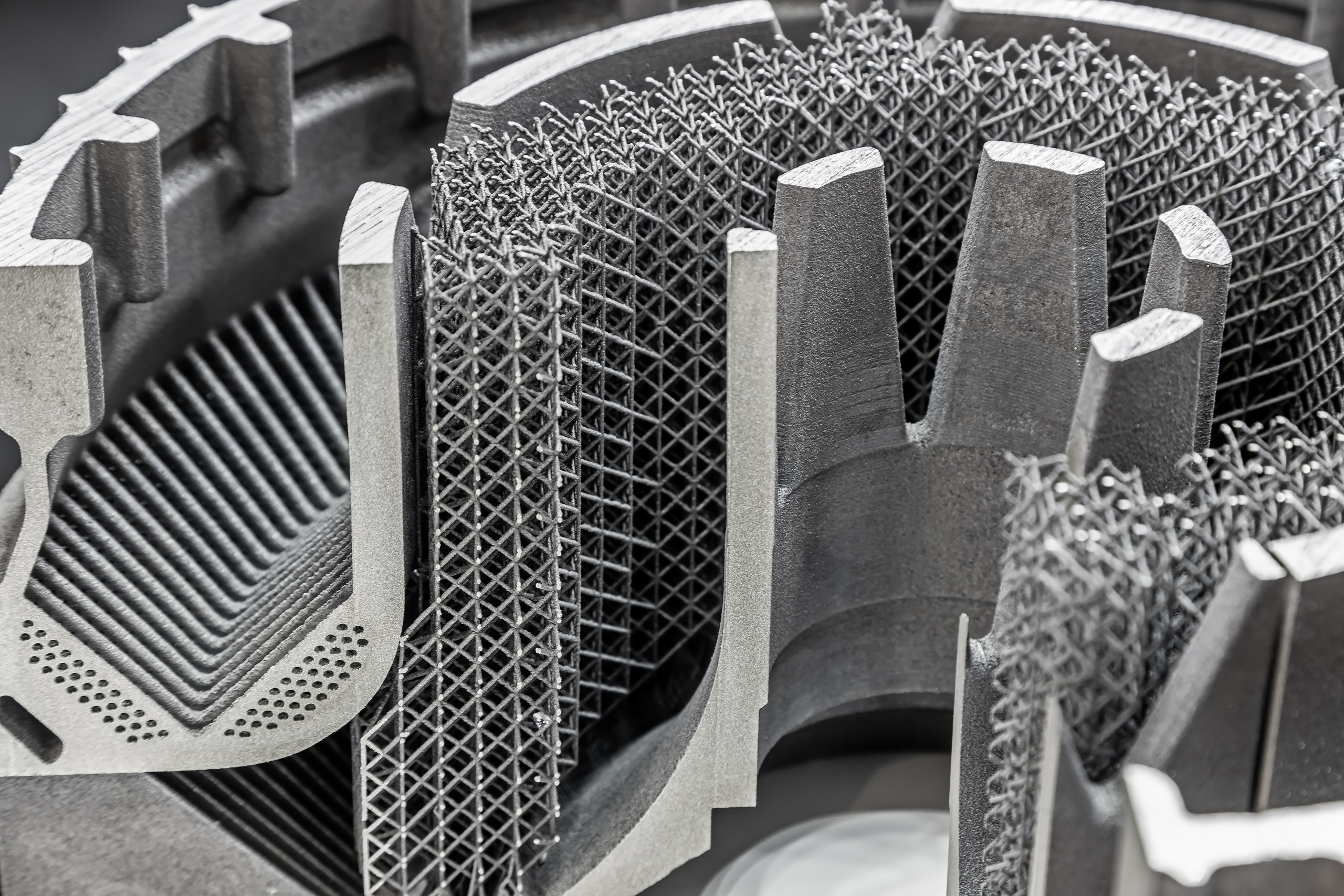
All aspects of additive manufacturing and advanced manufacturing that have a high impact on the mechanical properties such as strength, ductility and fatigue properties of the resulting component will be covered in this workshop. The qualitative and quantitative understanding of the influence of process parameters, resulting microstructure and the mechanical properties are within the scope of this conference, as well as challenging application examples, machine improvement, new process developments and process monitoring.
Contact us
You have further questions or want to propose a topic?
Give our experts a call!



